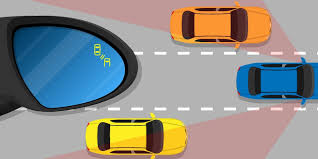
Driving on busy roads can be challenging, especially when it comes to navigating around other vehicles. One of the most common causes of accidents, particularly on highways and multi-lane roads, is the failure to spot other vehicles in a driver’s blind spot.
According to a report by Transport Accident Commission, blind spot-related accidents account for approximately 15% of all collisions on Australian roads.
This alarming statistic highlights the importance of technologies like blind spot monitoring that can significantly reduce the risk of such accidents.
In this article, we’ll explore what blind spot monitoring is, how it works, and why it’s a key feature for safer, smarter driving.
What is Blind Spot Monitoring?
Blind spot monitoring (BSM) is an advanced safety feature that uses sensors or cameras to detect vehicles that are not visible to the driver in the vehicle’s blind spots. These sensors are typically located on the side mirrors or near the rear bumper, where blind spots are most common. When another vehicle enters these areas, the system alerts the driver, usually with a visual or audible warning.
In modern vehicles, BSM is often integrated with other driver-assistance technologies, such as lane-keeping assist and rear cross-traffic alert, which further enhance safety by providing additional feedback and corrective actions.
How Does Blind Spot Monitoring Work?
The basic function of blind spot monitoring is to continuously monitor the area around the vehicle, particularly the zones that are difficult for the driver to see, such as the area just behind the side mirrors. Here’s a breakdown of how it typically works:
- Sensors or Cameras: BSM systems use radar sensors or cameras located on the sides of the vehicle or rear bumpers. These sensors can detect vehicles within a certain range and identify if they are in the blind spot.
- Warning Alerts: When a vehicle enters the blind spot, the system triggers a warning. This is usually a light that illuminates on the side mirror or a visual alert on the dashboard, informing the driver that there is a vehicle in the blind spot. In some cases, the system may also produce an audible warning.
- Active Intervention: Some advanced systems go a step further by actively intervening when the driver attempts to change lanes while a vehicle is in the blind spot. This could involve steering assistance to guide the car back into the correct lane or a haptic feedback warning via the steering wheel or seat.
Benefits of Blind Spot Monitoring
1. Enhanced Safety
The primary benefit of blind spot monitoring is the significant increase in road safety. Blind spots can be difficult to manage, especially when changing lanes at high speeds or on crowded highways. The visual and audible alerts provide drivers with real-time information, allowing them to make more informed decisions.
By reducing the likelihood of collisions caused by blind spot-related oversights, BSM technology contributes to overall road safety. As the Australian Road Safety report notes, this feature can be particularly beneficial for drivers in urban settings or during highway driving, where vehicles are often close together.
2. Reduced Driver Stress
Constantly checking mirrors and over-the-shoulder can be mentally exhausting, especially during long drives. Blind spot monitoring takes some of this pressure off the driver, making the driving experience less stressful. This increased peace of mind can also help reduce fatigue on long trips.
3. Complementary to Other Safety Systems
When integrated with other systems like lane-departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and rear cross-traffic alert, BSM becomes part of a holistic safety system that helps prevent accidents and improves driver awareness. For example, if a driver is unaware of a vehicle in their blind spot and begins to change lanes, the system can automatically adjust the steering or speed to prevent a collision.
The Future of Blind Spot Monitoring
As automotive technology continues to advance, blind spot monitoring systems are becoming more sophisticated. Future systems may include 360-degree camera views, advanced radar systems, and artificial intelligence that can predict potential collisions based on driver behavior and external conditions. Additionally, we can expect to see more vehicles coming equipped with BSM as standard features, making it accessible to a larger range of drivers.
Blind spot monitoring is a crucial safety feature that significantly enhances road safety by alerting drivers to vehicles in their blind spots.
With accident statistics highlighting the risks of blind spot-related collisions, technologies like BSM offer valuable solutions to protect drivers and passengers.
As vehicle technology continues to evolve, blind spot monitoring will play a key role in the transition to smarter, safer driving.
Whether you’re driving in the city, on a long highway journey, or simply changing lanes on a busy road, this technology provides an extra layer of protection, making driving safer for everyone.